Dental Implants In Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
December 8, 2023
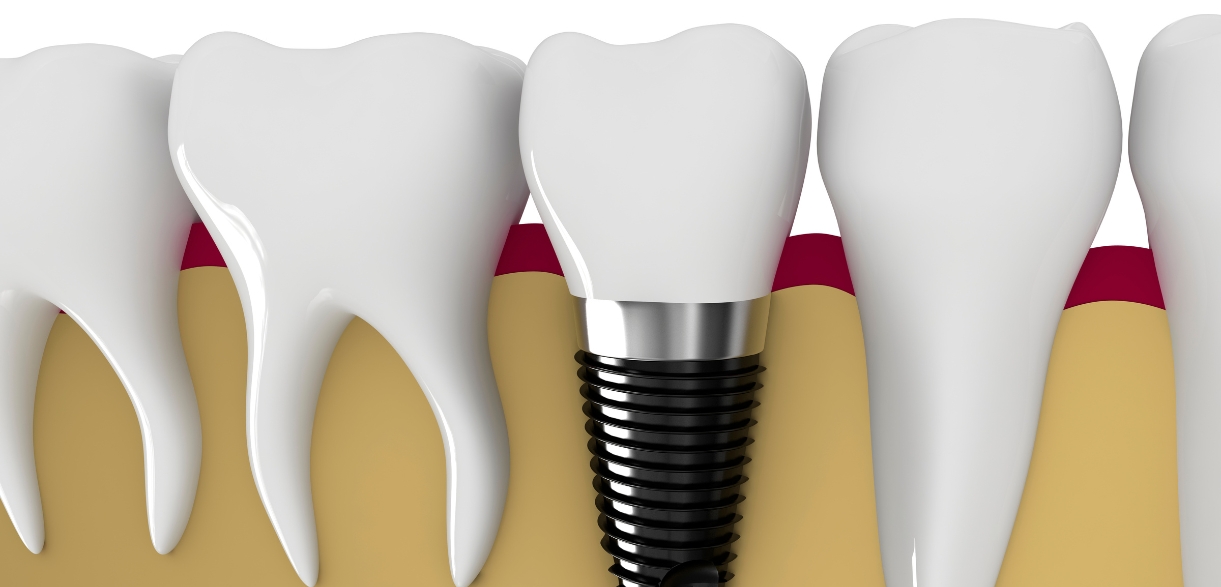
Dental Implants
Dental implants are a popular choice for replacing missing teeth, and luckily, the majority of individuals are good candidates for them. On the other hand, some medical issues raise red flags regarding this treatment. One such medical condition is rheumatoid arthritis To learn more about the impact of rheumatoid arthritis on dental implant eligibility, keep reading this guide.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by persistent inflammation that primarily targets the joints. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, resulting in inflammation, pain, swelling, and potential joint damage. RA typically affects symmetrical joints, such as wrists, knees, and fingers, and can also impact various organs and systems. Common symptoms include joint stiffness, fatigue, and a sense of overall discomfort. Timely diagnosis and effective medical management, often involving medications and lifestyle adjustments, are crucial for slowing the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and enhancing the overall well-being of individuals dealing with this condition.
While dental implants have proven to be beneficial for many RA patients, it is important to consult with your dentist to make sure they are a good fit for you.
Why is Rheumatoid Arthritis a concern for dental implant patients?
If you suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, your hands may become so affected that it becomes difficult for you to handle a toothbrush and floss your teeth thoroughly. You will be at a greater risk of dental implant failure if you do not practice adequate dental hygiene. This is due to the fact that a bacterial infection could enter your gums, destroy the tissue that surrounds an implant, and ultimately compromise the base of support for the implant.
Most treatments for rheumatoid arthritis involve suppressing the immune system, as it is an autoimmune disorder. In addition to the challenges of maintaining oral hygiene, inadequate cleaning can also heighten the likelihood of infection around the implants. Certain medications used to treat rheumatoid arthritis may have negative effects on bone health. Incorporating dental implants can be challenging for your body due to this. Long-term use of these medications can also lead to a decrease in bone density in the jaw, which can make it unstable and unable to adequately support a dental implant.
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Get Dental Implants?
The pivotal question remains: is it feasible for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis to undergo dental implant procedures? Let’s explore the considerations and factors that influence this decision.
Individualized Assessment: Every case is unique, and an individualized assessment is fundamental. The severity of RA, its impact on bone health, and the overall health of the patient must be evaluated comprehensively. Collaborative consultations between the rheumatologist and the dentist are essential to formulate a tailored approach.
Preoperative Planning: Thorough preoperative planning is paramount for success. This involves assessing the patient’s overall health, including their ability to manage inflammation and the potential impact of RA medications on the surgical process. Detailed imaging may be conducted to evaluate bone density and structure.
Collaborative Care: A multidisciplinary approach involving the rheumatologist, dentist, and oral surgeon ensures cohesive care. Open communication between these professionals helps create a treatment plan that considers both the dental and rheumatic aspects of the patient’s health.
Adaptations for Optimal Results: Adapting the implant procedure to accommodate the challenges posed by RA is a key consideration. This may involve modifications in the surgical approach, such as using a two-stage implantation process to allow for more extended healing.
Postoperative Monitoring: Individuals with RA may require vigilant postoperative monitoring to address any complications promptly. Regular follow-ups with both the rheumatologist and dentist ensure ongoing support and timely intervention if issues arise.
Individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can often get dental implants. However, it’s important for them to consult with their rheumatologist and dentist to assess their overall health and the severity of arthritis. The decision depends on factors such as the patient’s bone density, ability to heal, and medication regimen. Collaborative care between the rheumatologist and your dentist in Matthews, NC, ensures a comprehensive approach, addressing any potential challenges and optimizing the success of dental implant procedures for those with rheumatoid arthritis.
More Blog Posts
Composite vs. Amalgam Fillings: Which Is Better for Your Smile?
How to Know When Your Dental Crown Needs Replacement
Dental Crown Problems & How to Fix Them
Caring for Your Dental Crowns: Do’s and Don’ts